 |
AUFGABEN zu Differential-/Integralrechnung
|
Aufgaben zu
13. Winkelfunktionen
13.1 Bogenmaß
- Fülle die Leerstellen in der folgenden Tabelle aus
 in Grad in Grad |
10° |
|
|
23° |
514° |
|
1265° |
|
|
2° |
218° |
arc  |
|
1 |
0,1 |
|
|
2,56 |
|
0,724 |
75 |
|
|
Beachte: arc  =
=
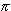 /180° ·
/180° ·  und
und
 = 180°/
= 180°/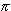 · arc
· arc 
13.2 Polarkoordinaten
- Zeichne
| a. |
P ( 2 ; 90° ) |
|
b. |
P ( 3 ; 180° ) |
|
c. |
P ( 2,5 ; -90° ) |
|
d. |
P ( 1 ; 520° ) |
| e. |
P ( 4 ; -1000° ) |
|
f. |
P ( 3 ; 2 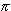 ) ) |
|
g. |
P ( 3 ; 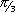 ) ) |
|
h. |
P ( 2 ; -2 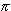 /5 ) /5 ) |
13.4 Eigenschaften der trigonometrischen Funktionen
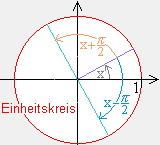
- Bergründen Sie am Einheitskreis folgende Beziehungen
- sin (-x) = - sin x (die Funktion sin ist ungerade)
- cos (-x) = cos x (die Funktion cos ist gerade)
- sin ( x + ½
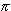 ) = cos x ) = cos x
- cos ( x - ½
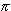 ) = sin x ) = sin x
- sin ( ½
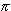 - x ) = cos x - x ) = cos x
- cos ( ½
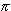 - x ) = sin x - x ) = sin x
- sin² x + cos² x = 1
- sin ( x + 2
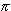 ) = sin x ) = sin x
- cos ( x + 2
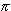 ) = cos x ) = cos x
Die Funktionen sin und cos haben die Periode 2 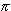
- Welche Periode haben die Funktionen tan und cot ?
|
 |
- Schreibe alle Nullstellen auf
| a. |
sin x |
|
b. |
cos x |
|
c. |
tan x |
| d. |
sin 2 x |
|
e. |
sin ½ x |
|
f. |
sin ( x + 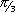 ) ) |
| g. |
sin ( 2 x + 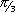 ) ) |
|
h. |
sin ( x/3 - 2 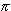 ) ) |
|
i. |
cos ( 3 x + ½ 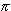 ) ) |
- Welche Periode haben die Funktionen
| a. |
y = sin 2 x |
|
b. |
y = cos x/2 |
|
c. |
y = cos ( - 2 x ) |
|
d. |
y = tan x/3 |
13.5 Streckung von sin-Kurven in x- und y-Richtung
- Zeichne je eine Periode der Kurve
| a. |
y = - 2 sin x |
|
b. |
y = 3 cos x |
|
c. |
y = 2 cos ( x - 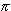 /6 ) /6 ) |
| d. |
y = 4 sin ( 3 x + 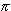 ) ) |
|
e. |
y = ¼ cos ( x/2 - 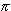 /2 ) /2 ) |
- Zeichne durch Überlagerung (Addition) zweier Kurven
| a. |
y = sin x + cos x |
|
b. |
y = sin x + 2 sin 2 x |
| c. |
y = x + sin x |
|
d. |
y = x² + sin x |
| e. |
y = 2 sin x + 3 cos x |
|
f. |
y = cos x/2 + sin 2 x |
- Im Dreieck ABC seien
 ,
,
 und a gegeben.
Berechne b und beweise so den Sinussatz.
und a gegeben.
Berechne b und beweise so den Sinussatz.
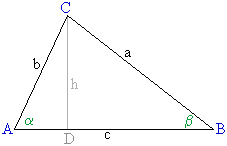
- Im Dreieck ABC seien b , c und
 bekannt.
Bestimme a und beweise so den Cosinussatz.
bekannt.
Bestimme a und beweise so den Cosinussatz.
| |
a² = b² + c² - 2 b c ·
cos  |
13.6 Additionstheoreme
- Berechne die Sehne s auf zwei Arten:
| a. |
Nach dem Cosinussatz aus 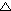 0AB 0AB |
 |
| b. |
Nach dem Satz des Pythagoras aus  ADB. ADB. |
| |
Zeige: |
| B D | = cos  - cos
- cos  |
| |
|
| A D | = sin  - sin
- sin  |
| c. |
Durch Gleichsetzung der beiden Werte für s² erhält man das Additionstheorem. |
| |
( A ) |
cos (  -
-  ) =
cos ) =
cos  · cos
· cos  + sin
+ sin  · sin
· sin  |
- Ersetzt man
 durch ( -
durch ( -  ) , erhält man aus ( A ) in Aufgabe 10.:
) , erhält man aus ( A ) in Aufgabe 10.:
| |
cos (  +
+  ) =
cos ) =
cos  · cos
· cos  - sin
- sin  · sin
· sin  |
- Leite aus Aufgaben 10. und 11. die Additionstheoreme
| |
sin (  +
+  )
= sin )
= sin  · cos
· cos  +
cos +
cos  · sin
· sin  |
und |
sin (  -
-  )
= sin )
= sin  · cos
· cos  - cos
- cos  · sin
· sin  |
her. |
Setze dazu in ( A ) für  ( 90° -
( 90° -  ) und danach
( -
) und danach
( -  ) für
) für
 .
.
- Leite aus den Additionstheoremen her:
| a. |
sin 2 = 2 cos = 2 cos
 sin sin  |
|
b. |
cos 2 =
cos² =
cos²  -
sin² -
sin²  |
| c. |
tan (  ± ±
 ) ) |
|
d. |
tan 2  = = |
2 tan  |
|
 |
1 - tan²  |
| e. |
sin²  =
½ ( 1 - cos 2 =
½ ( 1 - cos 2 ) ) |
|
f. |
cos  =
2 cos² =
2 cos²  /2 - 1 /2 - 1 |
- Zeige:
| |
sin x + sin y = 2 · sin |
x + y |
· cos |
x - y |
 |
 |
| 2 |
2 |
| |
sin x - sin y = 2 · sin |
x - y |
· cos |
x + y |
 |
 |
| 2 |
2 |
(Hinweis: Setze x =  +
+
 und
y =
und
y =  -
-
 und wende geeignete Additionstheoreme an.)
und wende geeignete Additionstheoreme an.)
weitere Aufgaben zu
13.7 Lineare Approximation der sin-Funktion
 zurück zu MATHEMATIK Übersicht
zurück zu MATHEMATIK Übersicht



![]()